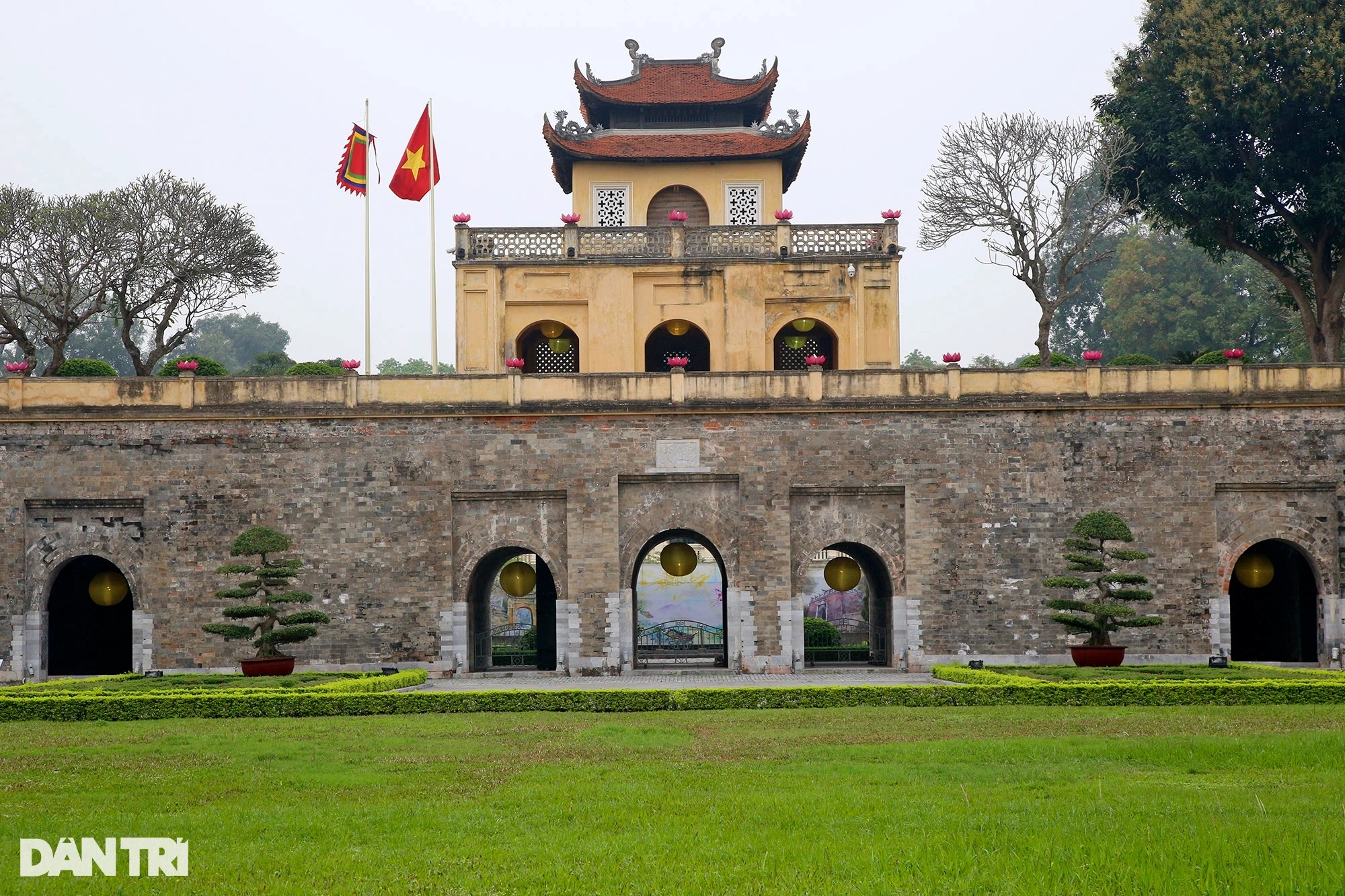
The Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long (Vietnamese: Hoàng thành Thăng Long) is a complex of historic imperial buildings located in the center of Hanoi, Vietnam. It was first constructed in 1011 under the reign of Emperor Lý Thái Tổ of the Lý dynasty.
The history:
The royal enclosure was first built during the Lý dynasty (1010) and subsequently expanded by the Trần, Lê, and finally the Nguyễn dynasty. It remained the seat of the Vietnamese court until 1810 when the Nguyễn dynasty chose to move the capital to Huế. The ruins roughly coincide with the Hanoi Citadel today.
The royal palaces and most of the structures in Thăng Long were in varying states of disrepair by the late 19th century with the upheaval of the French conquest of Hanoi. By the 20th century, many of the remaining structures were torn down. Only in the 21st century are the ruined foundations of Thăng Long Imperial City systematically excavated.
In mid-1945 the Citadel was used by the Imperial Japanese Army to imprison over 4000 French colonial soldiers captured during the Japanese coup d’état in French Indochina in March 1945: 19–20
The central sector of the imperial citadel was listed in UNESCO’s World Heritage Site on July 31, 2010, at its session in Brazil, as “The Central Sector of the Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long – Hanoi".
Relics:
The royal palaces and edifices were largely destroyed in the late 19th century. The few remaining structures within the royal compound are the Doan Mon gate, marking the southern entrance to the royal palace, the Flag Tower, the steps of Kinh Thiên Palace, and the Hậu Lâu (Princess’ Palace).
Remains of the Imperial City were discovered on the site of the former Ba Đình Hall when the structure was torn down in 2008 to make way for a new parliament building. Various archaeological remains unearthed were brought to the National Museum to be exhibited. Thus far only a small fraction of Thăng Long has been excavated.